Patterns & Data 1: Intro to Patterns & Data
< Back to Building Block
In order to see the importance of patterns, you must make use of data and in order to make use of data, you must also understand the importance of patterns. Data can be collected on any body of work. Data collection can come in the form of anecdotal student feedback on a project, tracking student grades on a bell curve to assess the appropriate amount of rigor, or on a large scale for organizations and governments to determine the effectiveness of their initiatives.
What is the purpose of this exercise?
Those who collect data will tell you that all the data in the world will mean nothing if it is not organized and presented meaningfully. Patterns (repeating similarities among objects, ideas, and problems) allow analysts, students, teachers, researchers, etc. to find and give meaning to their data so it can be presented to others.
In this exercise, you will study how patterns formulate and how to make use of them. You will explore how information is represented by computers, and look at ways to engage students with data oriented tasks in order to help them notice trends. You will also address the use of patterns in creative tasks in future exercises.
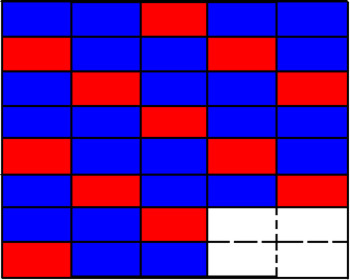
In this unit when we discuss patterns, we are talking about Pattern Recognition! Pattern Recognition is the process of analyzing data and identifying the similarities and connections among the different pieces of the larger problem. Patterns help us solve complex problems efficiently. In order to make use of a pattern one must recognize, identify and make use of a pattern. Pattern Recognition helps break down the problem and also build a construct as a path for the solution.
Reflection
The image above is an example of a pattern recognition test. What patterns do you see in this image?
Due to our increasing connectedness, and the inexpensive nature of sensors and computer storage, we generate data at an almost unfathomable rate. Within this data are patterns that can be hard to detect by humans. Modern machine learning techniques can allow computers to look for patterns and learn about underlying behaviors, but this process benefits greatly from a human understanding of how patterns can be detected.
Another important part of the data representation process is being able to generate visuals that help us to digest information more easily. The art of visualizing information is something that humans excel at. Finding patterns in data is the first step to determining what we want to show in our visuals.
With computational thinking, pattern recognition occurs as people study a problem and decompose it. Computational tools allow us to explore, analyze, interpret, and synthesize massive amounts of data faster than a human ever could. We can use computational methods such as data mining (examining large databases) and data federation (combining data sources) to discover new trends, patterns, and links in our understanding and appreciation of humankind.
One way to engage in patterns is to represent and visualize data, which can help simplify the complexity of data and convey the message. Watch the clip below of a TEDtalk from 2010 that discusses data visualization. While watching, consider how the speaker is using pattern recognition and data visualization to make use of the data he is studying.
The Beauty of Data Visualization - David McCandless

Whether or not you recognize it yet, ELA teachers are already well versed in the relationship between data and patterns. We read literature to identify interesting patterns in imagery, word choice, and so on. But data? Data might not be a word you hear often in ELA class, but that’s because we use different terminology: textual evidence, annotation, literary elements. These are all wonderful variations of how data operate in ELA.
Pattern and data practices in English Language Arts (ELA) focuses on identifying patterns in a given text, analyzing patterns to draw conclusions, and making comparisons between different texts.
Example of Patterns in ELA: Literary Analysis
When conducting literary analysis, a reader might look for patterns in the style of authors, organization of writing, or even word choice. Focusing on patterns would allow the reader to make a detailed analysis and provide insights into the text itself. Pattern matching can also be used to develop linguistic understanding and improve writing style.
Example of Patterns in ELA: Parts of Speech
Using patterns to understand the usage of parts of speech would assist with improved writing skills. Using patterns to track common writing mistakes can assist writers with proofreading and self-editing of writing.
Example of Data in ELA: Literary Research
In terms of data practices in ELA, writers collect data, analyze data, and communicate data as part of the research process. Using data visualization tools, writers can easily analyze data they have collected to draw conclusions to communicate in writing or they can use data visualization as a unique form of communication. Data practices and pattern matching can also be used by readers and authors to identify missing perspectives in the landscape of literature.
In Social Studies, we don’t only look at the past, we also look at the present and future. Studying data helps us identify the patterns between social/historical events to explain and/or make predictions on the analyzed phenomena.
Patterns and Data in a Historical Context
Researchers, political scientists, museum curators, and sociologists are always using pattern recognition to look for patterns in their areas of expertise and rely on data practices to be systematic in their collection, analysis, and communication of that data. One might consider how common economical, political, and social issues repeat themselves across different historical civilizations.
Patterns and Data in a Predictive Context
The use of political polls in the election process is an excellent example of how patterns and data practices are used in the field of social studies.
Demographers design surveys, administer those surveys, and publish the reports. The results of these reports influence campaign spending decisions, speechwriters, and can also affect public opinion. Digital tools offer a variety of ways to publish data providing visualization that convey their own messages. Combining different visualizations can provide deeper insights into how different sources of data might be related which, in turn, can impact campaign decisions or candidates’ platforms.
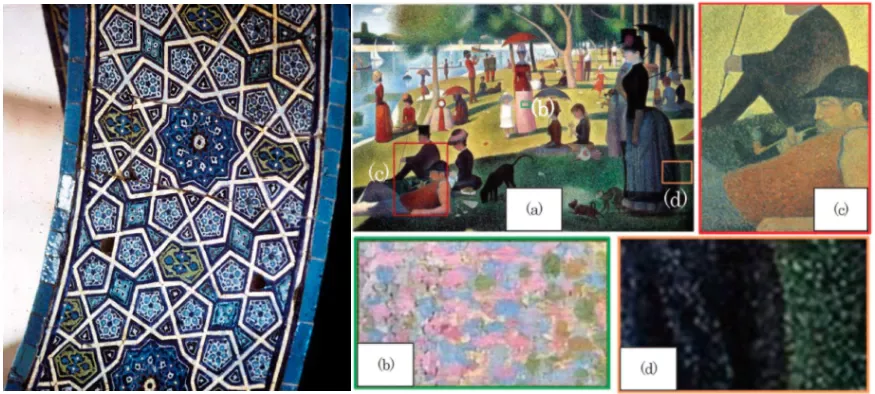
In the Arts, a pattern is a repetition of a specific element. Musical compositions often contain patterns of notes that repeat in the melody. Visual pieces of art contain colors, lines, dots, shapes, etc. that repeat to form patterns. Looking for patterns in visual arts and performing arts to better understand and interpret artistic work is an essential part of analysis for any observer.
Examples of patterns in visual arts can be analyzed across cultures and time. For instance, the images above show two examples of patterns being used in different ways. On the left, we see an archway in the Green Mosque of Bursa, Turkey created in 1424. This archway contains a repeating pattern with 10-point stars and pentagons. On the right, we see Georges Seurat's 1886 painting "A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte". In this piece of art, we see a painting technique called pointillism. In pointillism, small, distinct dots of color are applied in patterns to form an image. Callouts B-D show the detail of the technique in specific areas of this painting.
When creating original art and music, considering how patterns are a fundamental part of the creative process. Modern multimedia artists are using patterns to create unique pieces of art based on data they collect in places such as weather patterns, status updates, and urban planning. These techniques of collecting data and using them to distinguish patterns can relate to the creative processes your students engage with in the classroom. Consider the type of data and patterns they can collect from their classmates and how that can affect their artistic work.
There are several examples of recognizing patterns in data for problem-solving in everyday life and across the curriculum. In addition to the examples in previous steps, this article from Equip Learning (article found here) provides great context that can assist you in answering the reflection questions below.
Reflection
☞ Although your students may not understand how Netflix’s pattern recognition algorithm works, how can you use this example to help your students begin to identify patterns in everyday life?
☞ This activity showcased several examples of pattern recognition across different classroom subjects. Of these examples, which one resonated with you the most and why? Explain how this activity may impact your classroom.
